Such coatings or films are denoted henceforth as polyelectrolyte multilayers pems.
Dynamic viscoelasticity in polyelectrolyte multilayers nanodamping chem mat.
Schlenoffdynamic viscoelasticity in polyelectrolyte multilayers.
Dynamic viscoelasticity in polyelectrolyte multilayers.
We report on the time dependent viscoelastic response of nanoblended films of a polyelectrolyte complex prepared by the multilayering method.
Mat sci eng c bio s.
A 370 2004 pp.
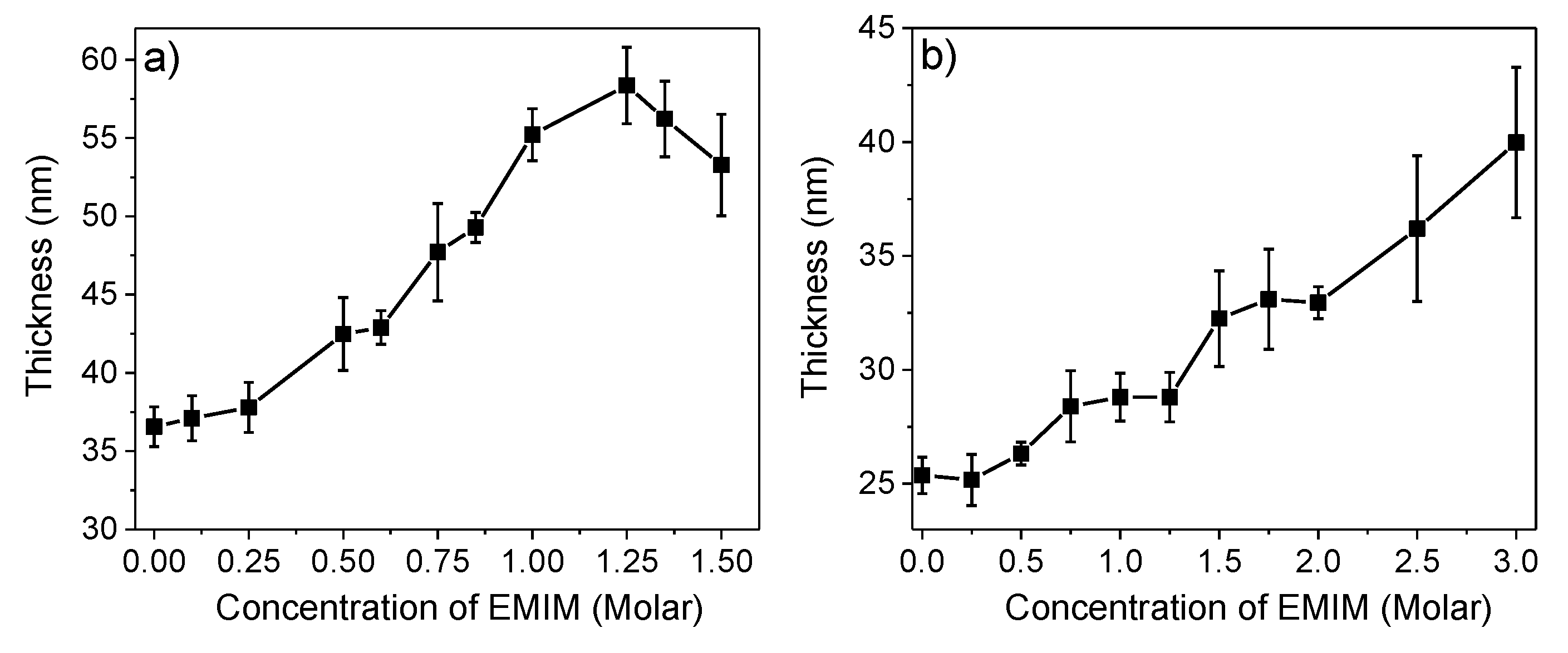
Polyelectrolyte multilayers pem obtained by layer by layer assembly can be doped with ionic liquid il via the swelling of the films with il solutions.
Mater 18 2006 pp.
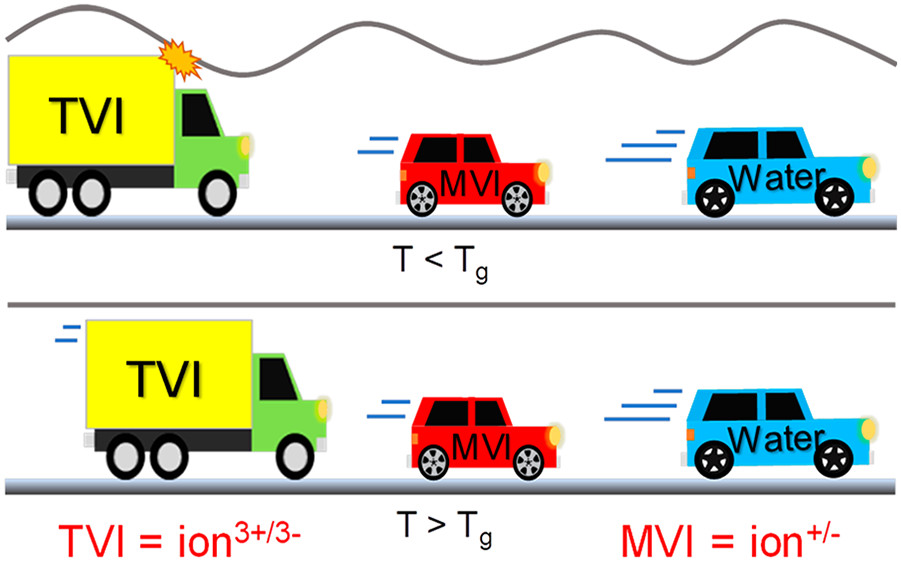
The ion pairing interactions within polyelectrolyte multilayers pemus are reversibly broken by adding salt to the electrolyte in which the pemu is immersed.
Dynamic viscoelasticity in polyelectrolyte multilayers.
1 3 pems self assemble due to electrostatic interactions between sequentially deposited alternately charged pes.
2 4 6 the chemical composition and concentration of.
Thus the bulk modulus of these ultrathin films may be regulated without changing temperature.
This unprecedented ability to fine tune a multilayer to be either cell adhesive or bioinert along with the unique feature of controllable porosity allows polyelectrolyte multilayers to be envisioned for membranes controlled release and biocompatible implant coating applications.
The sequential layer by layer adsorption of polycations and polyanions was shown to be an extremely versatile and facile technique for the preparation of polyelectrolyte multilayers pem on a variety of substrates since their discovery in 1991 by decher and co workers they have received considerable attention such systems have an obvious practical value but they are.
The specific ion effect on the growth of polyelectrolyte multilayers can be observed in.
L ayer by layer lbl assembly of polyelectrolytes pes is a method for preparing highly tunable thin film polymer coatings.
In order to examine the mechanical properties of il containing pem we implement a kelvin voigt model to obtain thickness viscosity and elastic modulus from the frequency and dissipation shifts determined by a dissipative quartz crystal.
Two flexible oppositely charged polymers can form liquid like complex coacervate phases with rich but poorly understood viscoelastic properties.
They serve as an experimental model system for many biological and man made materials made from oppositely charged macromolecules.
Experimental and mathematical modeling investigation on the dynamic viscoelasticity behavior of free liquid films prepared by alpha olefin sulfonate.